Mozart malware was first spotted this February by the security researcher Vitali Kremez. Mozart is a form of malicious software that uses DNS protocol to contact a remote server and communicate with its developers. The threat falls into the category of malware loaders, which means that it could be used to execute various commands on infected computers and avoid detection by security software.
Table of Contents
How is Mozart Malware Distributed?
The developers of Mozart malware usually distribute it via phishing emails with malicious PDF documents that link to a ZIP file located at https://masikini[.]com/CarlitoRegular[.]zip. This ZIP file contains a JavaScript file that when executed, will extract a base64 encoded executable which is saved to the victim's computer as %Temp%\calc.exe and executed later on.
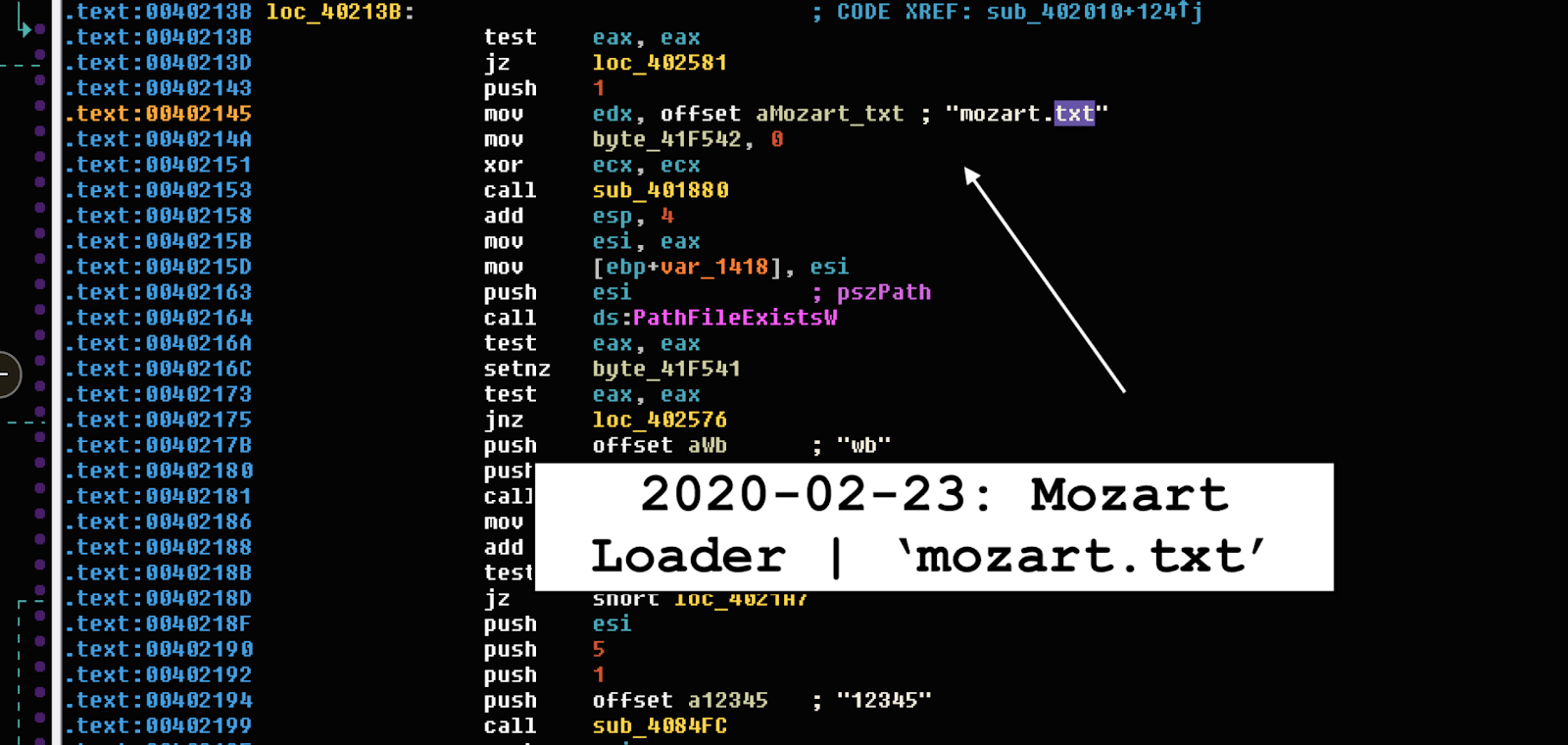
Figure 1: Image: Mozart Loader
Static analysis showing Mozart malware loader being pushed to the system. Source: malware.news
Other malicious attachments that hackers use to infect computers are MS Office documents, executable files, archive files, and JavaScript files.
The other methods used for spreading Mozart malware are by using fake software updaters, unofficial software activation ('cracking') tools, malicious downloads from untrustworthy sources, and Trojans.
- Fake software updaters – they infect systems either by exploiting flaws of outdated programs installed on a targeted machine or by installing malicious software instead of legitimate updates.
- Software 'cracking' tools - some people use unofficial programs to bypass paid activation of licensed software. Unfortunately, these tools are dangerous as hackers often use them for distributing malware.
- Untrustworthy software channels - hackers use them as tools to host malicious files and disguise these files as legitimate. When downloaded and opened, they infect victims' computers with malicious software.
- Trojans - cybercriminals are well aware that if installed onto a system, trojans can cause severe chain infections. For that reason, hackers often use programs of this type for installing malware.
How Does Mozart Malware Work
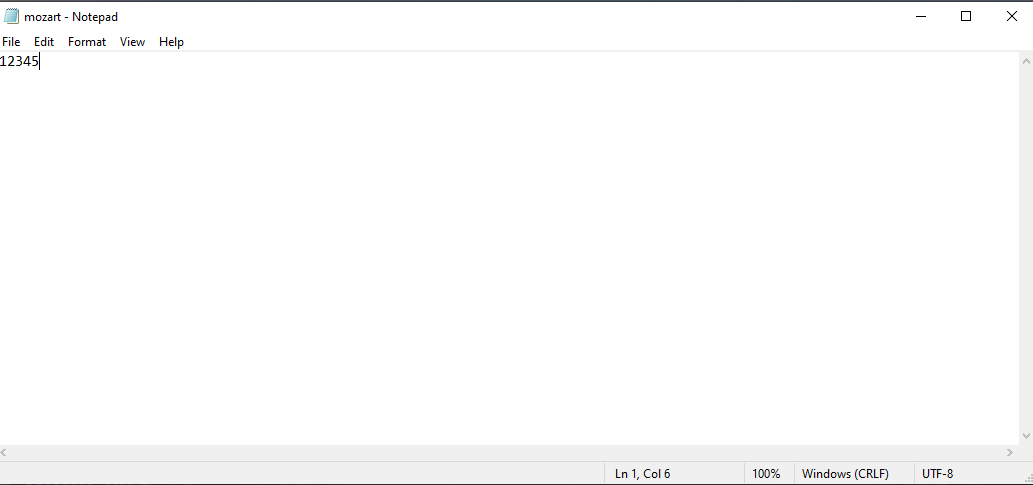
The founder of Mozart malware, Vitali Kremez claims that once onto the system, the backdoor will first check for the file %Temp%\mozart.txt and if it doesn't exist, the malware will create this file with the contents of '12345' and make some preparations on the targeted machine.
The preparation work includes copying the calc.exe file from the %Temp% folder to a random named executable in the %AppData%\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\ folder that will startup every time the victim logs into Windows.
Figure 2: Mozart Text File
Mozart text file containing the numbers 1 through 5.
Kremez explains that Mozart malware will also communicate with a hardcoded DNS server controlled by the hackers. The server, located at 93[.]188[.]155[.]2 issues the following DNS requests to receive instructions or configuration data:
The loader obtains the bot ID and returns Base64-encoded parameters for tasks and further processing:
A. ".getid" (.1)
The bot generation API sequence is as follows:
GetCurrentHwProfileW -> GetUserNameW -> LookupAccountNameW -> ConvertSidToStringSidW
B. ".gettasks" (.1)
Parse tasks with "," delimiter
C.".gettasksize" (.1)
Allocate memory for the task and dnsquery_call
D. ".gettask" (.1)
Parse for the specific task
E. ".reporttask" (.0|.1)
Run the task via CreateProcessW API
F. ".reportupdates" (.0|.1)
Retrieve and check updates via WriteFile and MoveFilW locally for a stored check as ".txt"
H. ".getupdates" (.0|.1)
Check for presence of ".txt" update and write the update with "wb" flag and check for executable extension (".exe") following with ".gettasks" call.
While analyzing Mozart, security researchers found that the malware constantly issues 'gettasks' queries to hackers' DNS servers to find commands to execute. In case the TXT record response is empty, the malware will keep performing the same check until a command shows up.
Having infected a computer, Mozart malware may cause plenty of serious problems such as data loss, identity theft, browsing safety, issues related to privacy, monetary, etc. Other examples of this type of program are Borr, Urelas, and GrandSteal.
How to Block Mozart Malware
Currently, there is no information on what commands are being executed by Mozart malware. However, considering the fact that this malware uses DNS protocol to communicate with its developers, malware experts suggest a way of blocking it.
To block Mozart malware, David Maxwell, Software Security Director at BlueCat, suggested:
"At your firewall, block outbound port 53 from everywhere except your official internal DNS server - this virus goes directly to a fixed external IP, and while you could just block that, the next virus won't use the same IP. Forcing all of your corporate name resolution to go through the resolvers you maintain gives you the ability to monitor traffic and control policy."
Also, be sure to enable DNS TXT queries if your security software can do it.





Leave a Reply
Thank you for your response.
Please verify that you are not a robot.